Introduction:
Cloud Computing, where data and applications are growing rapidly, cloud computing has emerged as a revolutionary solution. With its scalability, cost-effectiveness, and flexibility, cloud computing has changed the way businesses operate and the way individuals interact with technology. If you’re new to cloud computing or looking to expand your understanding, this comprehensive guide will walk you through the essentials, benefits, and frequently asked questions of using cloud computing.
[lwptoc]
Section 1: Understanding Cloud Computing
What is cloud computing?
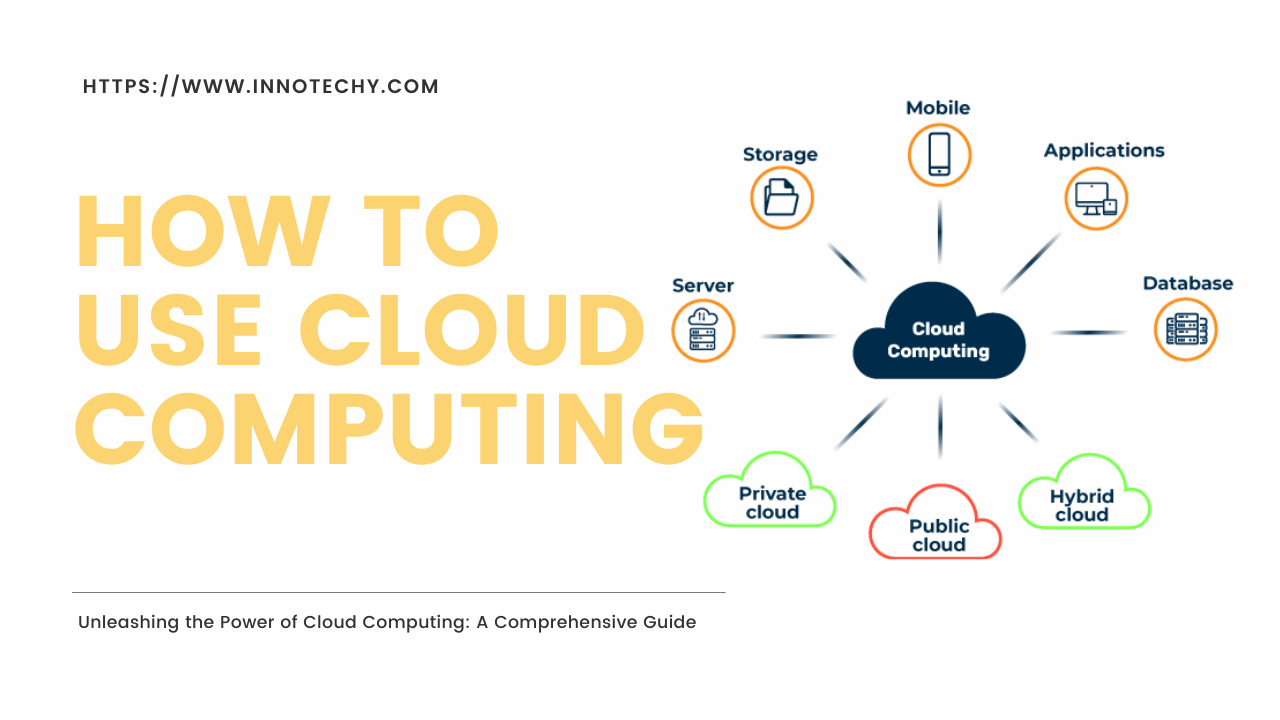
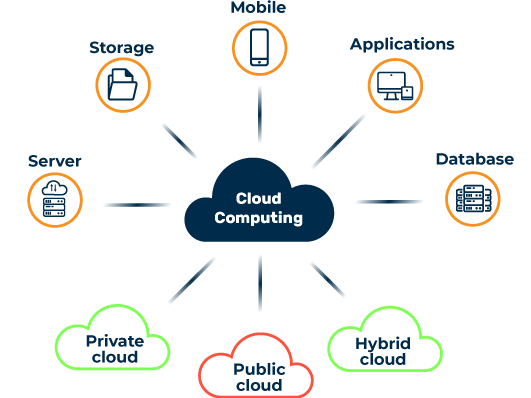
Cloud computing refers to the provision of computing resources, such as servers, storage, databases, networking, and software, on a pay-as-you-go basis over the Internet. It eliminates the need for local infrastructure and allows users to access and use resources remotely.
How does cloud computing work?
Cloud computing operates on a network of remote servers hosted in data centers around the world. Users access these resources through the Internet, enabling them to store, manage, and process data.
Types of cloud computing models
There are three basic cloud computing models:
Public Cloud: Services available to the general public, managed by third-party providers, and shared among multiple users.
Private Cloud: Resources are dedicated to a single organization and managed internally or by a third-party provider.
Hybrid Cloud: A combination of public and private clouds, provides greater flexibility and allows organizations to take advantage of the benefits of both models.
Section 2: Advantages of Cloud Computing
Scalability and flexibility
Cloud computing offers unparalleled scalability, allowing businesses to quickly scale up or down their resources based on demand. It provides flexibility by enabling users to access data and applications from anywhere using any device.
Cost-effectiveness
Cloud computing eliminates the need for initial hardware investment and reduces maintenance costs. Organizations can pay for the resources they use, optimizing their costs and avoiding unnecessary costs.
Better support and accessibility
Cloud computing facilitates seamless collaboration by enabling users to access, share and edit files simultaneously. This ensures data consistency and eliminates version control issues. Additionally, cloud-based applications and data can be accessed from anywhere, promoting remote work and increasing productivity.
Better security and disaster recovery
Cloud service providers prioritize data security and invest in robust infrastructure, offering sophisticated security measures, such as encryption, access control, and regular backups. Cloud computing also ensures data redundancy, reducing the risk of data loss due to hardware failure or natural disasters.
Section 3: Getting Started with Cloud Computing
Choosing the right cloud service provider
Choosing a reliable and reputable cloud service provider is very important. Consider factors such as reliability, security, scalability, support, and pricing models before making a decision.
Cloud deployment models
Evaluate the pros and cons of public, private, and hybrid cloud deployment models to determine which best aligns with your organization’s needs and goals.
Choosing the right cloud computing service
Different cloud computing services cater to specific needs. Explore offerings such as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) to find the right fit for your organization.
Section 4: Migrating to the Cloud
Assess your existing infrastructure
Before moving to the cloud, assess your existing infrastructure, applications, and data. Identify dependencies, performance requirements, and potential compatibility issues to plan a smooth migration process.
Developing a migration strategy
Create a migration strategy that includes prioritizing applications, determining the migration method (lift and shift, re-platforming, or rebuilding), and establishing a timeline and budget.
Best practices for data transfer
Ensure data integrity and security during migration by implementing appropriate backup procedures, encrypting data in transit and at rest, and conducting thorough testing and validation.
Section 5: Maximizing Cloud Computing Potential
Adoption of serverless computing
Serverless computing allows developers to focus on writing code without managing servers or infrastructure. It offers automated scaling, cost optimization, and improved development agility.
Leverage containerization
Containerization, using technologies such as Docker and Kubernetes, enables efficient deployment and management of applications. This ensures consistent performance across different environments and facilitates scalability.
Implementing auto-scaling
Autoscaling dynamically adjusts computing resources based on demand. It optimizes resource allocation, ensures optimal performance during peak loads, and reduces costs during low demand.
Section 6: Addressing Security Concerns
Data privacy and compliance
Understand the legal and regulatory requirements of your industry and ensure that the cloud service provider complies with relevant standards, such as GDPR or HIPAA. Implement encryption, access controls, and regular security audits to protect sensitive data.
Securing the cloud infrastructure
Implement strong security measures, such as strong authentication, multi-factor authentication, and network segmentation. Update software regularly and apply security patches to mitigate risks.
Backup and disaster recovery
Develop a comprehensive backup and disaster recovery strategy to protect your data in the event of system failure or disasters. Regularly test and verify the recovery process to ensure its effectiveness.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
What is the difference between public, private, and hybrid clouds?
Public cloud: Public clouds are open to the general public, and their infrastructure and services are managed by third-party providers. Users share these resources, resulting in cost-effectiveness and scalability. Public clouds are suitable for applications with low-security requirements and variable workloads.
Private cloud: Private clouds are dedicated to a single organization and can be managed internally or by a third-party provider. They offer better security and control over data, making them suitable for highly sensitive data or compliance-driven industries.
Hybrid Cloud: Hybrid clouds combine elements of both public and private clouds. Organizations can take advantage of the scalability and cost-effectiveness of public clouds while maintaining control over sensitive data in a private cloud environment. Hybrid clouds provide flexibility and allow businesses to optimize their infrastructure based on specific needs.
How does cloud computing save costs?
Cloud computing offers several cost-saving benefits:
No upfront hardware investment: Organizations can avoid significant costs associated with purchasing and maintaining on-premises infrastructure.
Pay as you go: Cloud providers offer flexible pricing options, allowing businesses to pay only for the resources they use. This eliminates the need for oversupply and reduces unnecessary costs.
Scalability and resource optimization: With cloud computing, businesses can easily scale their resources up or down based on demand. This ensures that resources are optimally allocated, preventing underutilization and associated costs.
What are common challenges in cloud migration?
Cloud migration can present some challenges, including:
Application Compatibility: Some legacy applications may require modification or re-platforming to be compatible with cloud environments. A thorough assessment and planning is essential to ensure a smooth migration process.
Data security concerns: Organizations must address data privacy and security concerns when migrating to the cloud. This includes choosing a reliable cloud service provider that complies with relevant industry standards and implements strong security measures.
Complex dependencies: Applications may have dependencies on specific hardware or software configurations. Identifying and addressing these dependencies is critical to successful migration.
Staff training: Cloud computing introduces new technologies and processes that may require training for IT staff. Ensuring that the team is equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge is essential for a seamless transition.
How does cloud computing differ from traditional IT infrastructure?
Cloud computing differs from traditional IT infrastructure in several ways:
Provision of on-demand resources: Cloud computing allows enterprises to access computing resources as needed, eliminating the need for local infrastructure and upfront investment.
Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud services provide the ability to scale resources up or down based on demand, offering unparalleled flexibility. Upgrading or downgrading traditional infrastructure often requires time and effort.
Pay as you go: Cloud computing follows a consumption-based pricing model, where organizations pay for the resources they use. Traditional infrastructure often involves significant upfront costs and ongoing maintenance costs.
Focus on core competencies: By leveraging cloud services, organizations can offload infrastructure management and maintenance to cloud providers, allowing them to focus on their core business objectives.
What are the best ways to improve cloud performance?
To improve cloud performance, consider the following best practices:
Monitor Resource Utilization: Continuously monitor and analyze resource utilization to identify bottlenecks, optimize configurations, and right-size resources.
Automation and Orchestration: Leverage automation and orchestration tools to streamline processes, improve efficiency and ensure a consistent supply of resources.
Implement caching and CDNs: Use caching mechanisms and content delivery networks (CDNs) to reduce latency and enhance content delivery to end users.
Continuous Optimization: Regularly assess your applications and infrastructure for performance bottlenecks. Improve code, configurations, and architecture based on performance metrics and user feedback.